XWorm v6.4 Edition: A Deep Dive into the Resurgent RAT Malware Threat
In the ever-evolving landscape of cybersecurity, threats like XWorm continue to adapt and pose significant risks to individuals and organizations alike. The XWorm v6.4 edition represents a notable update in this modular Remote Access Trojan (RAT) family, introducing enhanced plugins and persistence mechanisms that make it even stealthier. This article explores the intricacies of XWorm v6.4, its operational mechanics, and essential defense strategies to safeguard against it. Whether you’re a cybersecurity professional or simply concerned about digital safety, understanding this malware is crucial.
What is XWorm Malware?
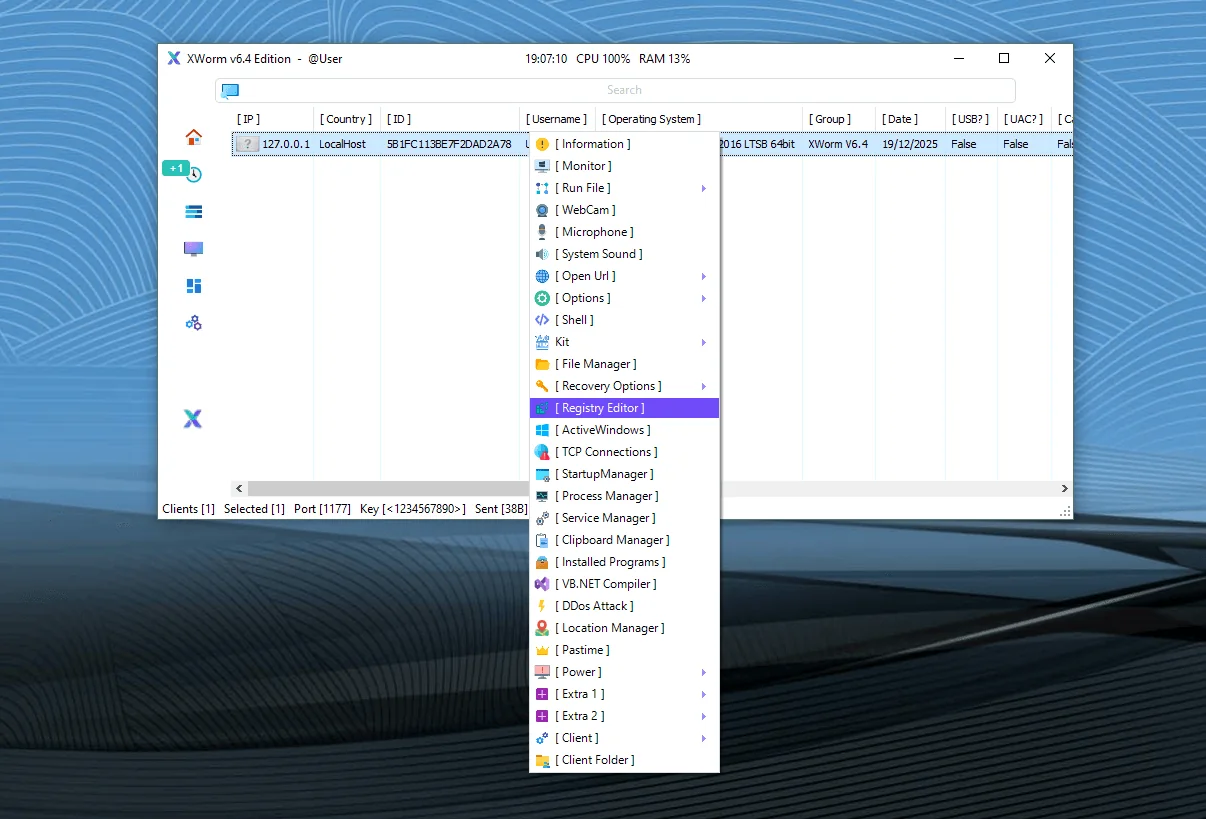
XWorm is a versatile Remote Access Trojan first observed in 2022, designed as a modular toolkit that allows cybercriminals to customize attacks based on their needs. It operates through a core client that communicates with command-and-control (C2) servers, enabling remote control, data exfiltration, and deployment of additional malicious payloads. Unlike traditional malware, XWorm’s strength lies in its plugin-based architecture, which supports over 35 functions for activities ranging from surveillance to ransomware deployment.
The malware generates a unique Client ID for each infected machine by hashing system details like processor count, username, machine name, OS version, and system directory size. This ID is pivotal for identification, plugin storage in the registry, and deriving encryption keys. XWorm v6.4 builds on previous versions by addressing vulnerabilities and incorporating cracked enhancements, making it a go-to tool for threat actors in underground forums.
The Evolution to XWorm v6.4 Edition
XWorm’s developer seemingly retired after version 5.6 in late 2024, but the malware resurfaced with v6.0 on June 4, 2025, marketed as a fully re-coded edition without the remote code execution (RCE) flaws of its predecessor. Priced at a one-time $500 lifetime subscription, v6.0 promised updated plugins and built-in persistence options. However, cracked versions quickly proliferated, leading to v6.4 iterations that include specialized additions like improved infostealing capabilities.
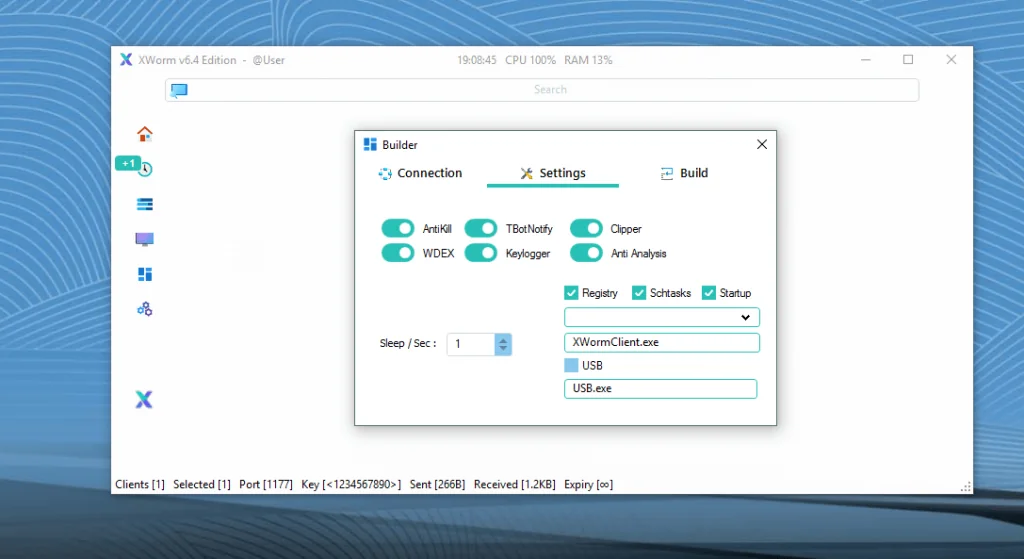
Key changes in XWorm v6.4:
- C2 Key Update: Shifted from “<123456789>” in v5.6 to “<666666>” for enhanced security.
- Plugin Enhancements: Introduction of SystemCheck.Merged.dll for stealthier browser data theft without injection.
- Cracked Features: Includes Rootkit.dll for process hiding and ResetSurvival.dll for persistence even after system resets.
This edition has seen a surge in VirusTotal submissions, indicating widespread adoption among cybercriminals. It’s often bundled with other threats like Remcos RAT or DarkCloud Stealer, amplifying its impact.
Key Features of XWorm v6.4
XWorm v6.4 excels in modularity, allowing operators to load plugins dynamically without leaving filesystem traces. The core client handles C2 communications via AES encryption, plugin management, and command execution. Here’s a breakdown of its standout features:
- Remote Control: Full system access, including keyboard/mouse simulation, screen captures, and webcam recording.
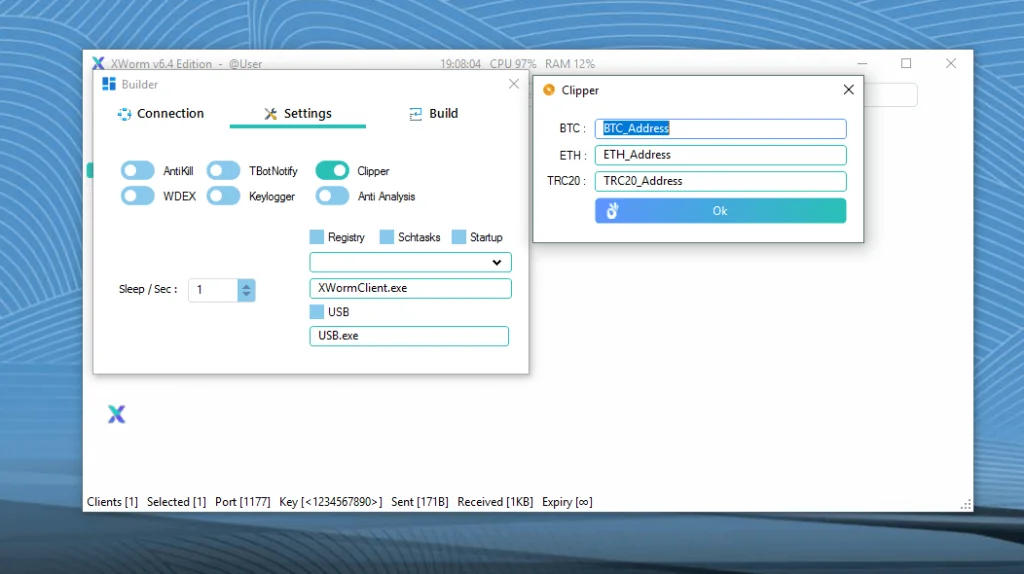
- Data Theft: Extracts credentials from browsers (Chrome, Firefox, Edge), WiFi passwords, Discord/Telegram tokens, and cryptocurrency wallets like MetaMask.
- File Management: Upload/download, encrypt/decrypt files using AES-CBC, and perform operations like locking or renaming.
- Network Recon: Lists and terminates TCP connections, gathers system information.
- Ransomware Integration: Encrypts files (excluding system directories) and demands payment via custom notes and wallpapers.
The malware’s ability to invoke plugins like “Run”, “RunRecovery”, or “ENC” ensures flexible operations tailored to the attacker’s goals.
Plugins in XWorm v6.4: A Modular Arsenal
Plugins are the heart of XWorm’s versatility, delivered as gzip-compressed DLLs stored in the registry under HKCU\SOFTWARE\. They are protected by tools like ILProtector and loaded in memory for evasion. Notable plugins in v6.4 include:
| Plugin Name | Functionality | Key Updates in v6.4 |
|---|---|---|
| RemoteDesktop.dll | Enables remote sessions, screenshots, input simulation, file drops. | Enhanced for hidden operations. |
| SystemCheck.Merged.dll | Steals browser data (cookies, passwords, credit cards) without injection; uses external decryption tools from GitHub. | New in v6.4 for bypassing Chrome v120 security. |
| Ransomware.dll | AES-CBC file encryption, ransom note deployment; shares code with NoCry Ransomware. | Anti-debugging checks added. |
| Shell.dll | Remote command execution via hidden cmd.exe. | Supports “runshell” and “closeshell” commands. |
| FileManager.dll | File operations, AES encryption/decryption using Client ID-derived keys. | FTP upload and hash calculation. |
| Rootkit.dll (Cracked) | Hides processes prefixed with “$CRX”. | Exclusive to cracked v6.4 editions. |
| ResetSurvival.dll (Cracked) | Ensures re-infection post-Windows reset via ResetConfig.xml. | Adopted from other RATs like Pulsar. |
Other plugins like Webcam.dll, Clipboard.dll, and HVNC.dll support surveillance and interaction, making XWorm a comprehensive threat toolkit.
Infection Chain: How XWorm v6.4 Spreads
The typical infection chain for XWorm v6.4 starts with social engineering tactics like phishing emails containing malicious JavaScript or VBScript files.
- Initial Dropper: A JS or VBS file downloads a PowerShell script while displaying a decoy PDF to distract the user.
- AMSI Bypass: The PS script disables Antimalware Scan Interface (AMSI) by patching CLR.DLL in memory, evading detection.
- Payload Delivery: Downloads the XWorm client and an injector DLL, which injects the malware into a legitimate process like RegSvcs.exe.
- C2 Connection: Establishes contact with servers (e.g., 94.159.113.64:4411) using the key “P0WER” or “<666666>”.
- Plugin Deployment: Requests and executes plugins as needed, often leading to secondary infections.
In some variants, the VBScript uses obfuscation with ChrW conversions and eval for execution, further complicating analysis.
Persistence and Evasion Techniques in XWorm v6.4
Persistence is a hallmark of XWorm v6.4, ensuring long-term access:
- Registry Run Keys: Adds entries like “Onedrives” or “Winlog” pointing to batch/PS1 files in %TEMP% or %APPDATA%.
- Logon Scripts: Uses UserInitMprLogonScript for execution on login.
- Reset Survival: Employs ResetConfig.xml in C:\Recovery\OEM to survive factory resets, a technique borrowed from advanced RATs.
Evasion tactics include:
- Memory-only execution to avoid disk writes.
- Anti-analysis checks: Terminates on Windows XP, detects sandboxes via IP-API queries, and flags as critical process to cause BSOD on kill attempts.
- Browser bypass: Spawns external processes for data theft without triggering alerts.
- Debugger detection: Uses CheckRemoteDebuggerPresent and handle enumeration for Sandboxie.
These methods make XWorm v6.4 particularly challenging for traditional antivirus solutions.
How to Defend Against XWorm v6.4
Protecting against XWorm v6.4 requires a layered security approach:
- Endpoint Security: Deploy EDR tools to monitor process injections, registry changes, and anomalous network traffic.
- Email and Web Filtering: Block malicious JS/VBS droppers and phishing attempts.
- Network Monitoring: Watch for C2 communications and plugin downloads; use firewalls to restrict ports like 4411.
- User Education: Train on recognizing phishing and avoiding suspicious downloads.
- Advanced Tools: Leverage solutions like Trellix for detonation analysis or Netskope for AMSI bypass detection.
Regular updates, multi-factor authentication, and threat intelligence feeds are essential to stay ahead of this RAT threat.
Download XWorm v6.4
Conclusion
XWorm v6.4 edition underscores the persistent innovation in malware development, blending modularity with sophisticated evasion to create a formidable cyber weapon. By understanding its features, plugins, and tactics, defenders can better mitigate risks. Stay vigilant—cybersecurity is an ongoing battle.
For more insights, check our cybersecurity tips or external resources on RAT prevention.
FAQ
- What is XWorm v6.4? A modular RAT malware with plugins for theft and control.
- How does XWorm v6.4 infect systems? Via phishing with JS/VBS droppers leading to PowerShell execution.
- Can XWorm v6.4 be removed? Yes, with EDR tools and registry cleanup, but prevention is key.