XWORM v2.2
XWORM v2.2
Features:
Builder :
Schtasks – Startup – Registry |
| AntiAnalysis – USB Spread – Icon – Assembly |
| Icon Pack |
Connection :
| Stable Connection – Encrypted Connection |
Tools :
| Icon Changer – Multi Binder [Icon – Assembly] |
| Fud Downloader [HTA-VBS-JS-WSF] – XHVNC – BlockClients |
Features :
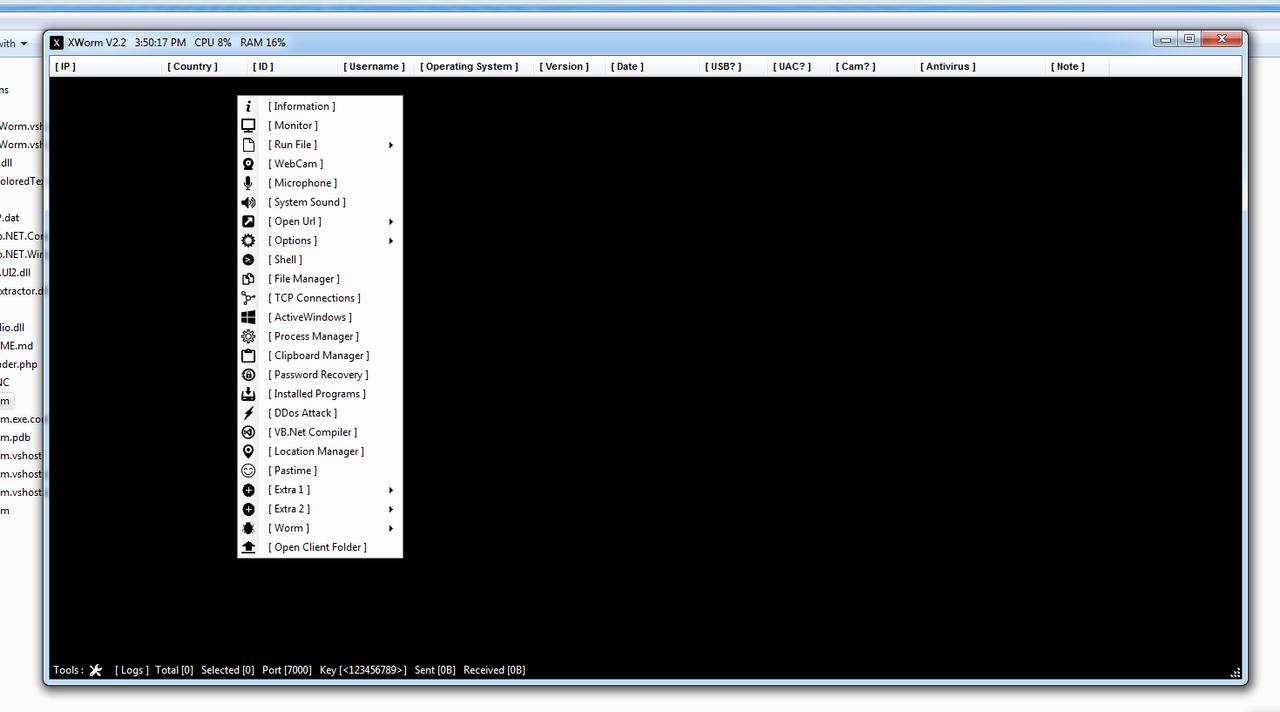
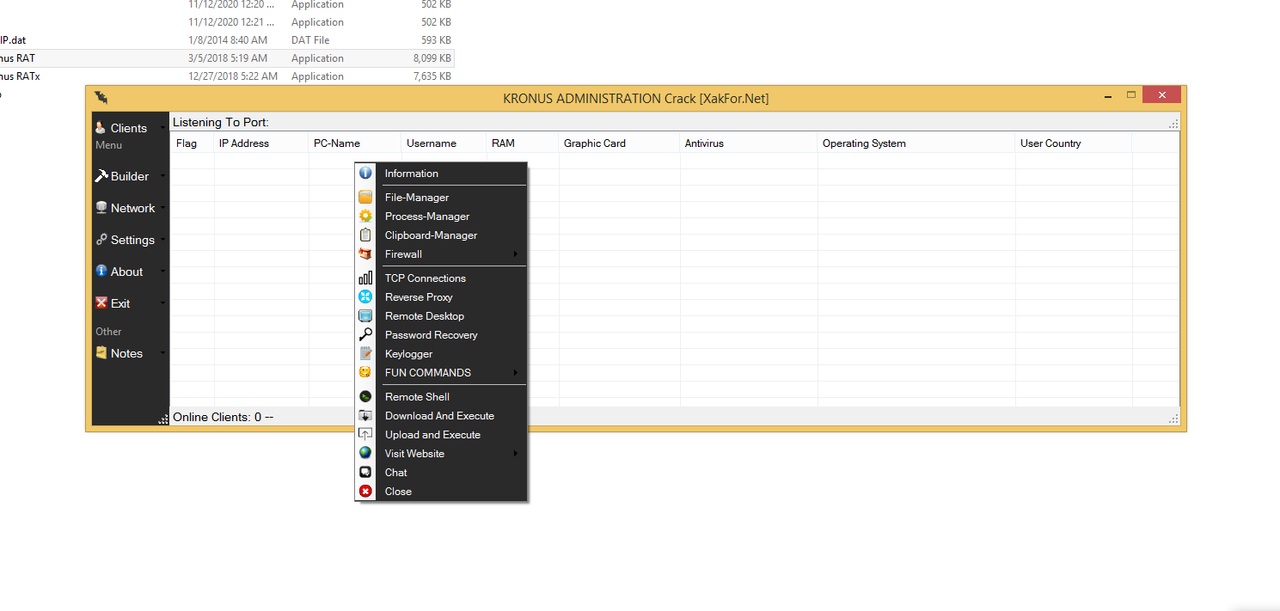
Information
Monitor [Mouse – Keyboard – AutoSave]
Run File [Disk – Link – Memory – Script – RunPE]
WebCam [AutoSave]
Microphone
System Sound
Open Url [Visible – Invisible]
TCP Connections
ActiveWindows
Process Manager
Clipboard Manager
Shell
Installed Programs
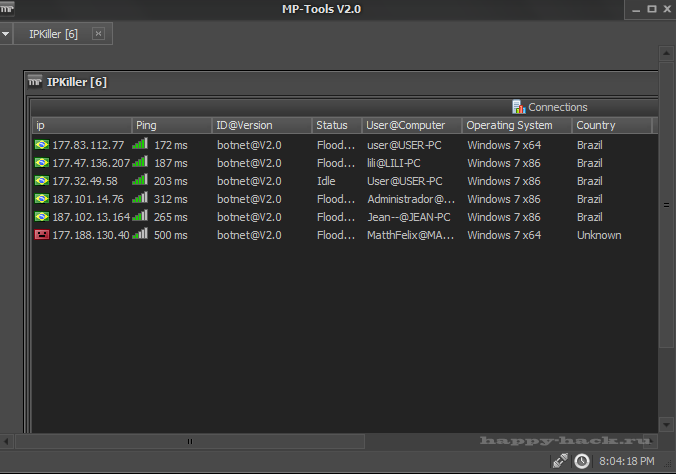
DDos Attack
VB.Net Compiler
Location Manager [GPS – IP]
File Manager
Client [Restart – Close – Uninstall – Update – Block – Note]
Options :
Power [Shutdown – Restart – Logoff]
BlankScreen [Enable – Disable]
TaskMgr [Enable – Disable]
Regedit [Enable – Disable]
UAC [Enable – Disable]
Firewall [Enable – Disable]
.NET 3.5 Install
Disable Update
Run Shell
Invoke-BSOD
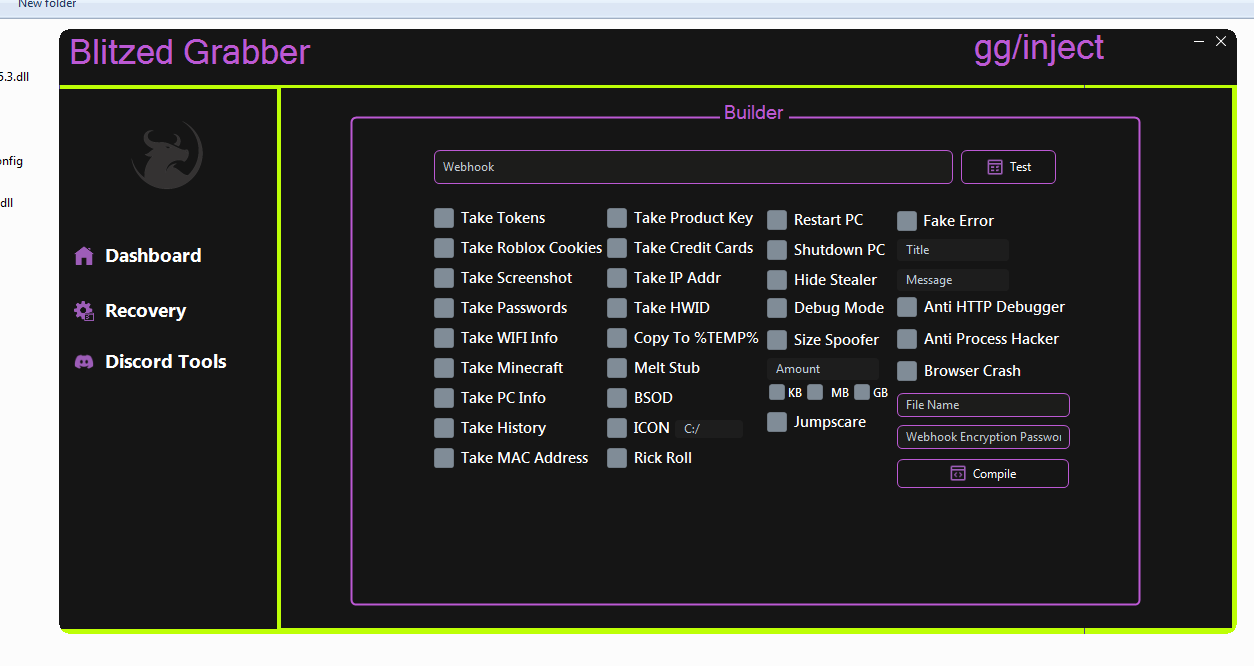
Password Recovery :
| FileZilla – ProduKey – WifiKeys – Email Clients |
| Bookmarks – Browsers – All-In-One – DicordTokens |
Pastime :
CD ROOM [Open – Close]
DesktopIcons [Show – Hide]
SwapMouse [Swap – Normal]
TaskBar [Show – Hide]
Screen [ON-OFF]
Volume [Up – Down – MUTE]
Start [Show – Hide]
Clock [Show – Hide]
Text Speak
Explorer [Start – Kill]
Tray Notify [Show – Hide]
Extra 1 :
KeyLogger
Client Chat
FileSeacher
USB Spread
Bot killer
PreventSleep
Message Box
Change Wallpaper
DeleteRestorePoints
UAC Bypass [RunAs – Cmstp – Computerdefaults – DismCore]
Run Clipper [All Cryptocurrencies]
Extra 2 :
Ransomware [Encrypt – Decrypt]
Ngrok Installer
HVNC
Hidden RDP
WDDisable
Install [Startup – Registry – schtasks]